Lunchtime Read: The Fat Truth - How Unsaturated Fatty Acids Can Lead to Healthy Aging
While fat has gained a negative reputation in healthcare, it's essential to recognize the significance of healthy fats for promoting longevity and overall well-being.
Fat has often been given a bad rap, but did you know that not all fats are created equal? In fact, some fats are essential for our health and can even lead to healthy aging. Let's explore into the world of unsaturated fatty acids and discover how they can be a key player in our well-being.
The Good, the Bad, and the Fatty
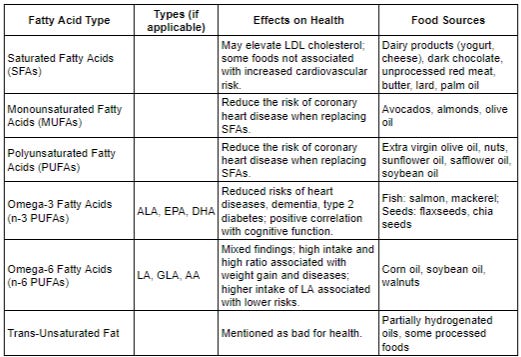
Fats are essential for our health. They provide essential fatty acids and help our bodies absorb vitamins like A, D, and E. But not all fats are the same. They can be classified into three types:
Saturated Fats (0 double bonds): Often linked to bad cholesterol and heart diseases.
Monounsaturated Fats (1 double bond): These can reduce the risk of heart diseases.
Polyunsaturated Fats (>1 double bonds): These include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are vital for our health.
The Debate: Are Saturated Fats Really Bad?
Recent studies have shown that some foods rich in saturated fats, like yogurt, cheese, dark chocolate, and unprocessed red meat, may not increase the risk of heart diseases. The complex nutritional profiles of these foods, including vitamins, probiotics, minerals, and proteins, might be the reason.
However, replacing saturated fats with monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fats has been shown to reduce heart disease risks. So, the question remains: Are saturated fats bad, or is it about what we replace them with?
The Good Fats: Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Unsaturated fatty acids, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, have been shown to have positive effects on health. Here's why they're so important:
1. Heart Health:
Replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats can reduce the risk of heart diseases.
Foods like olive oil and nuts, rich in unsaturated fats, have been linked to lower heart disease risks.
2. Omega-3 and Omega-6:
These essential fatty acids are vital for our brain and heart.
Omega-3 (found in fish and flaxseed) has been linked to reduced risks of dementia and heart diseases.
Omega-6 (found in corn and sunflower oil) has mixed effects, with some types reducing inflammation and others possibly promoting it.
3. The Balance Game:
The ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 in our diet matters.
A high ratio may lead to weight gain and diseases, while a balanced intake can have beneficial effects.
The Global Perspective
Different parts of the world have different eating habits, and this affects the intake of these essential fatty acids:
South Asia: High omega-6 intake, low omega-3 intake, resulting in an unhealthy ratio of 50:1.
Western Diet: Typical ratio of 20:1.
Recommended Intake: Around 250 mg/day of seafood omega-3.
In many regions, the intake of omega-3 is lower than recommended, which may require increasing seafood consumption or supplementing with high-quality fish oils.
The Ongoing Debate
While the benefits of unsaturated fats are clear, there's still debate about saturated fats. Some recent studies have found that foods like yogurt, cheese, and dark chocolate, rich in saturated fats, may not increase heart disease risks. This has led to calls for more specific guidelines on reducing certain types of saturated fats rather than an overall reduction.
Conclusion: Embrace the Good Fats
The world of fats is more complex and fascinating than it might seem. Unsaturated fatty acids, including omega-3 and omega-6, are essential for our health and can play a vital role in healthy aging.
So, don't fear the fat! Embrace the good ones, understand the balance, and enjoy the delicious journey towards a healthier and longer life. Whether it's enjoying a piece of salmon or adding a splash of olive oil to your salad, these good fats might just be the secret ingredient to a vibrant and healthy life.



