Goodbye, Painful Bones! How These Tiny Powerhouses Are Revolutionizing Bone Healing
The Rise of Extracellular Vesicles as a Safer, Faster Alternative to Stem Cell Therapies for Degenerative Bone Conditions
Are you tired of the long waits, risks, and complexities that come with traditional stem cell treatments for degenerative bone conditions? Discover how Extracellular Vesicles, the microscopic wonders, are turning the tide, offering faster, safer, and more efficient options for bone regeneration. Your future of pain-free living might just be a small vesicle away! (Estimated Read Time = 15 minutes)
Introduction
Degenerative bone disorders are medical conditions that cause your bones and the cushiony parts between your bones to gradually weaken and break down. These include ailments like osteoarthritis, which impacts your joints, and osteoporosis, which makes your bones brittle and more prone to fractures. As you can imagine, these conditions can severely impact a person's quality of life, causing pain, making movement difficult, and often leading to a decline in overall health. These are especially concerning for older people, but they can affect anyone at any age. Despite advances in medical science, there are still only limited treatments for these disorders, and most don't provide a long-term fix.
Lately, there's been a new ray of hope in medical research for treating these conditions, thanks to something known as stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles or, in simpler terms, special tiny bubbles produced by stem cells. These stem cells have the ability to transform into many different types of cells in the body, and the tiny bubbles they release contain a mixture of helpful substances. When introduced into areas of the body where bones and tissues are deteriorating, these tiny bubbles seem to send signals that help start the healing process.
For example, a group of researchers discovered that these tiny bubbles from a specific type of stem cell were able to help heal spinal cord injuries by promoting something called autophagy. This is a process where the body cleans out damaged cells and regenerates new ones, a kind of self-repair system for cells. The findings suggest that these tiny bubbles could potentially help in repairing not just spinal cord injuries, but also degenerative bone conditions like osteoarthritis and osteoporosis.
Because of the powerful healing signals these stem cell-derived tiny bubbles send, scientists and doctors are excited about their potential for treating a variety of illnesses, including those that affect the bones. Unlike traditional treatments that mostly aim to relieve symptoms, the use of these tiny bubbles represents a shift toward harnessing the body's own ability to heal itself.
In this article, we delve deeper into this new and exciting field of medicine. We'll explore how these special tiny bubbles could be used for treating common bone disorders that affect many people. Specifically, we will focus on understanding the underlying processes that make these tiny bubbles so effective and discuss how they could be applied in treating osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and other related conditions.
By exploring this captivating area of research, we aim to bring to light the potential benefits of these tiny but powerful bubbles in revolutionizing how we approach the treatment of degenerative bone disorders.
Isolation and Characterization of EV's, and Their Roles in Intercellular Communication
Definition and Characteristics of EVs
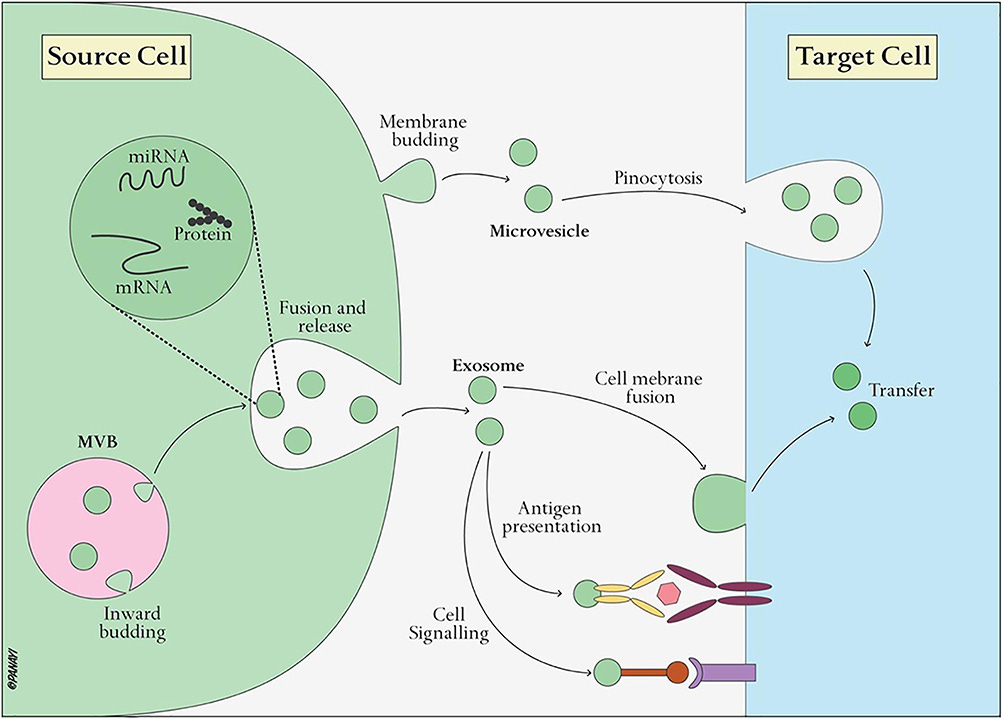
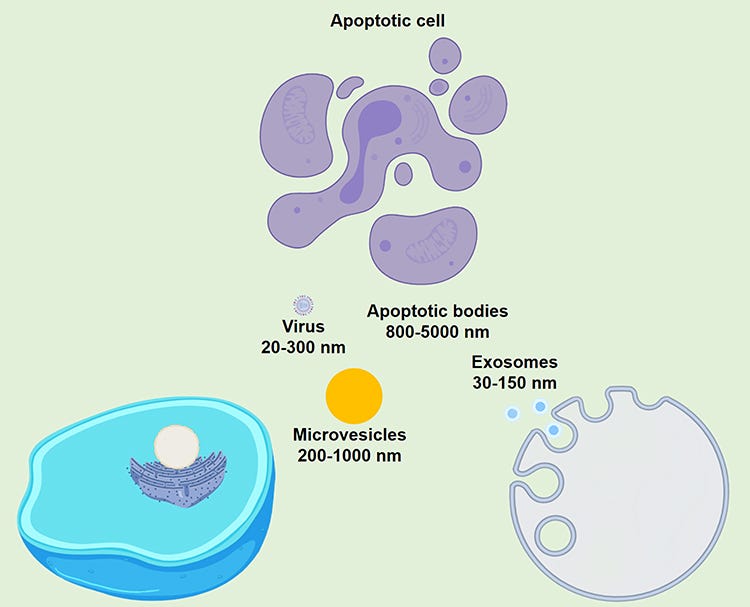
In the fascinating world of how cells talk to each other, there is something really special called EVs, or Extracellular Vesicles. Imagine these as tiny bubbles that come from cells. These tiny bubbles are not all the same; they can be very different from each other. Some are called microvesicles, some are known as exosomes, and others are named apoptotic bodies. Each of these kinds has its own unique features, like how they're made and what they do. Scientists find these differences really interesting.
These tiny bubbles do a lot of work in the body. They help keep things balanced and can even help cells decide what to do when someone is sick. Inside each tiny bubble are different things like fats, proteins, and special coding molecules (nucleic acids) that are picked to do certain jobs. These materials inside the tiny bubbles help them talk to other cells and tell those cells how to act.
Composition of EVs: Proteins, Lipids, and RNAs
In these tiny bubbles, there are different kinds of things packed inside them. Proteins are one of those things, and they do a lot of work in the body. For example, there are special kinds of proteins that help new blood vessels grow, which is important when the body needs to heal itself.
Fats, or lipids, are also in these tiny bubbles. They help keep the tiny bubbles whole and also play a role in talking to other cells. They help control things like swelling and growth of new blood vessels, and they are really important in helping the body heal.
There are also different kinds of coding molecules, called RNAs, inside these bubbles. These RNAs can go into other cells and either become new proteins or control how other proteins are made. This is another way these tiny bubbles can tell other cells what to do.
Interplay of Metabolic Effects, Inflammation, Cellular Crosstalk, and Osteogenic Activity
Now, when it comes to forming new bone, that's a pretty complicated process. Different things like the foods we eat, our body's health, and how cells talk to each other all play a part. For example, being very overweight or having diabetes can make it hard for new bone to form. Also, different chemicals in our body, made by fat cells, can either help or hurt the growth of new bone.
Inflammation, or swelling, is also a big part of this. Some cells that are part of the immune system can either help new bone grow or stop it from happening. And there's a lot of back-and-forth talking between different types of cells in the bones. Some cells make materials that help build bone while others break it down. Even blood vessels are important, as they make a place where new bone cells can grow.
Active Role of EVs in Stem Cell Therapy
These tiny bubbles also have an important role when it comes to stem cell therapy. Stem cells are like the body's repair kit, and these tiny bubbles help them do their work. They can help cells move, grow, and change in ways that help heal damaged or sick parts of the body.
What makes these tiny bubbles better than just using regular cell messages is that they can carry a lot of different materials inside them to do many things at once. Also, they are less likely to cause problems with the immune system. And these tiny bubbles are very good at going exactly where they need to go in the body.
Transfer of EVs' Cargo to Target Cells and Its Biological Effects
So how do these tiny bubbles talk to other cells? When they reach the cell they're supposed to talk to, they can stick to it or even go inside it. Once they're there, they release the special materials they were carrying. These materials then start chain reactions inside the cell that can make the cell change what it's doing. For example, some of the materials can stick to the outside of the cell and change what that cell does. Other materials can go deep inside the cell and give it new instructions.
So you see, these tiny bubbles called Extracellular Vesicles have a really big job. They're like the cell's messaging service, but they do more than just deliver messages. They can help cells change and do new things, which is important for keeping the body healthy and for helping it heal when it's not.
Extracellular Vesicles, or EVs, are small packages from stem cells that offer a promising new way to treat bone problems. Unlike using stem cells, EVs are easier to collect and pose fewer risks, making them a groundbreaking option in the field of regenerative medicine. While challenges remain, ongoing research is paving the way for EVs to become a major player in future treatments.
Sources of Stem Cell-Derived Small Bubbles for Bone Healing
Small Bubbles from Special Cells Found in Various Tissues
Think of these special cells, called Mesenchymal Stem Cells, as "master cells" that can turn into different types of cells in our body like bone, cartilage, and fat. These master cells are like a treasure chest found in different places like bone marrow, body fat, the umbilical cord from newborns, and even in the placenta during pregnancy. These cells make tiny bubbles that are filled with important biological stuff that helps in healing.
Bone Marrow as a Source
The insides of our bones, known as bone marrow, are like factories for these tiny healing bubbles. They contain a cocktail of important things, such as proteins and other types of molecules, that can help repair bones, control the body's defense system, and even make new blood cells. Some research shows these bubbles from bone marrow may be useful in treating certain diseases and conditions that involve our defense system.
Body Fat as a Source
The small bubbles coming from body fat have their own special ingredients, including growth helpers and immune regulators, which can speed up bone healing. These bubbles are being studied for their usefulness in repairing bones and tissues and treating certain diseases that affect our muscles and bones.
Umbilical Cord as a Source
The jelly-like substance inside the umbilical cord is also a great place to find these special cells and their tiny bubbles. The bubbles made from these cells are really good at controlling the body's defense responses and helping tissues to repair. They are being looked at as a way to treat conditions that make your bones weak, help wounds heal faster, and treat immune diseases.
Placenta as a Source
During pregnancy, the placenta acts like a support system for the baby. It has different kinds of cells that also produce these tiny healing bubbles. These bubbles are filled with a wide range of important biological things needed for the baby to grow and for the mother's body to accept the baby. More than that, these bubbles are rich in factors that encourage tissue growth, which makes them really interesting for studies about repairing bones and other tissues.
Lower Risks Compared to Using Cells Directly
Using these tiny bubbles may be better than using the master cells themselves for treating conditions. Why? Because it avoids some risks, like turning into the wrong cell type or being rejected by the body. These bubbles can be collected and stored for future use, and they can be given to patients in simple, less painful ways.
Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cell-Derived Tiny Bubbles in Fixing Worn-Out Backbones and Joints
The Problem with Backbones as We Age (IVDD)
The backbone is made of bones called vertebrae that are cushioned by soft discs. As we grow older, these discs can wear out, leading to a condition called Intervertebral Disc Degeneration (IVDD). This problem is worsened by age, lack of nutrition to the discs, and too much strain or stress on the backbone. Sometimes, it can even cause these cushioning discs to break down. The result is a lot of discomfort and loss of flexibility in the spine. Right now, we can only manage the pain, but we can't really fix the core issue.
How Tiny Bubbles from Stem Cells Can Help
Scientists are exploring ways to actually heal the backbone, and one exciting idea is using tiny bubbles, called extracellular vesicles (EVs), that come from stem cells. These EVs carry special healing substances that can help to repair the damaged discs in the backbone. They can:
Help create new cushioning material for the discs.
Calm down the swelling and irritation in the damaged area.
Help the cells in the damaged discs stay alive for a longer time.
This is groundbreaking because it doesn't require putting new cells into the body, but rather uses the healing power of these tiny bubbles to help fix the problem.
Making It Work in Real Life
Some researchers have even made a special gel that can deliver these healing tiny bubbles directly to the damaged discs. This is really important because it makes sure the bubbles go exactly where they need to, increasing the chances of a successful treatment.
The Problem of Sore Joints (OA)
As people get older, their joints, like knees and elbows, can also get damaged due to age and too much use. This is called osteoarthritis (OA). It involves the breakdown of the cartilage, the soft tissue that helps bones glide over each other. When this happens, the bones rub against each other causing pain. This is made worse by substances in the body that cause inflammation and further damage.
The Promise of Tiny Bubbles for Sore Joints
Just like with IVDD, these stem cell-derived tiny bubbles can also help with OA. They can:
Help create new cartilage, the soft tissue that cushions joints.
Reduce the harmful substances that make the condition worse.
Help the cells in the cartilage to live longer and work better.
Researchers have shown that these tiny bubbles can actually help the cartilage to grow back, offering a potentially transformative way to treat OA.
Weak and Fragile Bones (OP)
Finally, osteoporosis (OP) is another condition that makes bones weak and easy to break. It is caused by an imbalance between two processes: the building of new bone and the removal of old bone.
As we age, the process that removes old bone can become stronger than the process that builds new bone. This leads to weaker bones that are easier to break.
Advantages of EV-Based Therapies Over Stem Cell Transplantation
When we talk about fixing damaged bones, one of the new ways we can do this is by using tiny packages called Extracellular Vesicles or EVs, that come from stem cells. These EVs are amazing because they don't have some of the issues we face when using actual stem cells.
For starters, when doctors try to use stem cells, they need a lot of them and getting enough can be a big task. The stem cells have to be taken out, grown in a lab, and checked to make sure they're okay to use. This takes a lot of work, time, and resources. But with EVs, it's different. They can be easily taken out from stem cells and we can get a lot of them without the same level of difficulty. This helps us get to the treatment faster, which is great for patients who need help right away.
Another big plus for using EVs is safety. While stem cells can do amazing things like repair damaged parts of the body, there is a small chance that they could grow in a way that leads to tumors. EVs don't have this risk. They carry important signals and substances that help in fixing damaged bones but don't cause tumors.
Challenges and Opportunities
As promising as EVs are for treating bone issues, we can't ignore that there are still things we need to figure out. First, we need to better understand how EVs really work. How do they deliver the substances that help bones heal? Researchers are working on understanding these fine details so that they can make EV treatment even more effective.
We also need to look at how EVs get taken up by the target areas in the body and what changes they make once they get there. We should compare EVs from different sources to know which ones work best. All this information will help us improve how we use EVs to treat bone diseases.
Then there's the matter of getting these treatments approved and making sure they are safe and effective. This involves a lot of work from different people, like scientists, companies, and government agencies. They all need to work together to set the rules for how EVs should be tested, made, and used in treatments.
In summary, while there are still hurdles to jump, EVs offer an exciting new way to treat bone problems. As we continue to study them and solve these challenges, we can expect better and safer treatments for patients in the future.
Reference: Jia Z, Zhang S, Li W. Harnessing Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for the Regeneration of Degenerative Bone Conditions. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:5561-5578 https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S424731